As a freelancer in the Philippines, you may wonder if you must file an income tax return (ITR). The short answer is yes, you do. Filing your ITR is not only mandated by law; it is also essential for managing the finances of your legal freelance business and ensuring that you do not face penalties down the line.
Today, we will explore everything you need to know about the ITR–the different types of tax returns, requirements, common mistakes to avoid, and more.
[lwptoc]What is the Income Tax Return?
The ITR is a document filed by individuals and businesses to report their income taxes, gained from various sources within the Philippines. It is a record of taxes for the taxable year, whether calendar or fiscal. This is an essential legal requirement for all individuals and businesses that earn an income within the country.
Types of Tax Returns in the Philippines
The Philippines has a variety of taxes that individuals and businesses need to be aware of. Here are the different types of taxes and their corresponding tax return forms:
Annual Income Tax Return (BIR Form 1700)
The Annual Income Tax Return (AITR) is filed by individuals who earn income only from compensation or business or professional activities. This is for employees who have worked for two or more employers within the same year.
Annual Income Tax Return For Individuals Earning Income Purely from Business/Profession (BIR Form 1701A)
BIR Form 1701A is for individuals who are earning solely from their business or professional services. According to the BIR, this form is for those under the graduated income tax rates with optional standard deduction (OSD) as mode of deduction OR those who opted to avail of the 8% flat income tax rate.
Annual Income Tax Return For Individuals (including mixed Income Earner), Estates and Trusts (BIR Form 1701)
BIR Form 1701 is an annual income tax return form that is filed by individuals who are engaged in trade or business, or practice a profession, including those with mixed income (i.e., individuals who earn both business income and compensation income). The annual income tax return summarizes all the transactions covering the calendar year of the taxpayer. This requirement is in accordance with Section 51 of the Tax Code, as amended.
Quarterly Income Tax Return (BIR Form 1701Q)
The Quarterly Income Tax Return (QITR) is filed by individuals engaged in trade or business in the Philippines. It is filed every quarter of the year.
Certificate of Final Tax Withheld (BIR Form 2307)
Freelancers frequently work with clients and businesses that must withhold taxes on certain payments. Clients in such circumstances must submit BIR Form 2307, commonly known as the Certificate of Final Tax Withheld at Source. This form plays a major role in the tax process, particularly when dealing with withholding tax on income payments.
As a freelancer, you may earn money from clients who are required to withhold taxes. BIR Form 2307 is an important document in this situation because it shows the final taxes deducted by your clients from your income payments. It is required for proper tax reporting and compliance.
Understanding BIR Form 2307 is extremely important for freelancers to account for the taxes that were previously withheld when completing their income tax returns. This certificate serves as proof of the taxes paid on behalf of the freelancer and adds to the overall tax liability after the fiscal year.

Requirements for Filing Income Tax Returns
Filing income tax returns requires several requirements. Check out the list below.
- Tax Identification Number (TIN)
- Previously filed quarterly and annual returns
- Income Documents: W-2 form, pay slips, certificates of compensation, business or professional income documents
- Expense Documents: Official receipts, bills, invoices, bank statements
- Record of Tax Payments: BIR Form 2307 or Certificate of Creditable Tax Withheld at Source
- Personal information: full name, address, birthdate, civil status
- Tax returns from previous years (if applicable)
- Supporting documents for deductions and/or credits claimed
- Electronic Filing and Payment System (EFPS) ID (if filing electronically)
- Bank details for direct deposit of tax refunds
- A signed and dated return by the taxpayer or authorized representative.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Income Tax Returns
Filing income tax returns can be challenging, and even the most diligent taxpayers can make mistakes that can result in penalties and fines. This section will discuss the common mistakes taxpayers should avoid when filing their income tax returns.
- Incorrect TIN or incorrect spelling of name
The TIN is an essential requirement for filing income tax returns, and any mistakes in the TIN or the spelling of the taxpayer’s name can cause delays in the processing of the return. Taxpayers should double-check their TIN and name spelling before submitting their tax returns.
- Incomplete or inaccurate information
Taxpayers should ensure that all the necessary information is provided in their income tax returns. Only complete or accurate information can result in delays in the processing of the return and, in some cases, an audit or investigation by the BIR.
- Failing to report all income sources
All income sources, including gross income from salary, business income, and investment income, should be reported in the income tax return. Taxpayers must ensure that they accurately report all their income sources and pay the corresponding taxes to avoid legal consequences.
- Overstating deductions or claiming invalid expenses
Taxpayers should only claim deductions for expenses that are valid and supported by proper documentation. Overstating deductions or claiming invalid expenses can result in legal consequences from the BIR.
- Failing to declare or underreporting taxable income
Taxpayers should declare all taxable income in their tax returns. Underreporting taxable income or failing to report it all together can result in penalties and fines.
- Filing the wrong type of tax return
Taxpayers should ensure they are filing the correct type of tax return based on their income source and tax status.
- Late filing or non-filing of tax returns
Filing tax returns on time is crucial for taxpayers who need a tax refund. Filing a tax return late may ensure the refund processing is completed on time, which can cause inconvenience to the taxpayer.
- Not paying the correct amount of taxes owed
Different tax rates and tax brackets exist for different income levels. Tax rates may vary depending on the income earned, whether from compensation, business or profession, or investments.
As such, taxpayers must ensure that they know the tax rates that apply to their specific type of income and that they pay the correct taxes based on those rates.
- Filing returns with mathematical errors
Taxpayers should ensure that their tax returns are free of mathematical errors. Mathematical errors can result in delays in the processing of the return or an audit or investigation by the BIR.
- Failing to keep proper records and receipts
Taxpayers should keep proper records and receipts to substantiate the amounts they report on their tax returns easily. This includes information on all sources of income, deductions, and credits claimed.
Accurate records also help taxpayers calculate their tax liability correctly and avoid underreporting or overreporting their taxable income.
- Not seeking assistance from a tax professional
Taxpayers who need clarification on the tax filing process or their tax obligations should seek assistance from a tax professional. Failure to seek help can result in tax errors that may impose penalties or legal consequences.
- Ignoring tax notices or failing to respond to BIR inquiries
Taxpayers should respond to tax notices or inquiries from the BIR promptly. Ignoring tax notices or failing to respond to BIR inquiries can be detrimental to your freelance business.

Tax Planning Strategies
As Benjamin Franklin famously said, “In this world, nothing can be said to be certain except death and taxes.” While taxes are unavoidable, you can minimize the amount you pay. Tax planning strategies involve making smart financial decisions throughout the year to reduce your tax liability.
Here are some key strategies to consider.
1. Keeping accurate records and receipts
Good record-keeping is essential for accurate tax reporting. Keep all receipts and records of income and expenses in a safe place. Digital record-keeping tools like Beppo can help you stay on top of your finances.
2. Properly classifying income and expenses
Knowing the difference between income and expenses is crucial. Proper classification helps you accurately report your income and expenses and avoid errors or discrepancies in tax filings.
3. Maximizing tax-deductible expenses
Deductible expenses reduce your taxable income, lowering your tax bill. Tax-deductible expenses include charitable donations, mortgage interest, and medical expenses. Make sure to keep track of all your deductible expenses throughout the year.
4. Planning for capital gains and losses
Capital gains are profits from assets like stocks, estates, and trusts engaged in trade. Capital losses are losses from selling those assets. By planning, you can minimize your capital gains taxes. For example, you can offset capital gains with capital losses.
5. Taking advantage of tax-free allowances and exemptions
Tax-free allowances and exemptions can significantly reduce your tax bill. Examples include:
- The standard deduction
- Total personal and additional exemptions
- Tax-free contributions to a retirement account
6. Deferring income to a later tax year
Deferring income can lower your tax bill, especially if you think you will be in a lower tax bracket next year. Consider deferring bonuses or other income until the following year.
7. Claiming tax credits
Tax credits are automatically reduced from your total tax directly. Some examples of tax credits include the child tax credit, education credits, and energy credits.
8. Making contributions to a tax-advantaged retirement plan
Contributing to a tax-advantaged retirement plan is a great way to reduce your taxable income. Not only do you save for retirement, but you also lower your tax bill.
9. Keeping up-to-date with tax laws and regulations
Tax laws and regulations change frequently. Keeping up-to-date with these changes can help you plan and make smart financial decisions throughout the year.
10. Seeking advice from a tax professional
A tax professional can help you navigate the complex tax code and identify tax planning opportunities. Consider hiring a tax professional if you have a complicated tax situation or want to maximize your tax savings.
11. Establishing a tax-efficient business structure
As you run your own freelance business, structuring it properly can help you reduce your tax bill. Consult a tax professional to determine which business structure is best for your situation.
12. Taking advantage of tax-deferred investments
Tax-deferred investments like annuities or municipal bonds can help you reduce your taxable income. These investments grow tax-free until you withdraw the money.
13. Considering the tax implications of major financial decisions
Major financial decisions like buying a house or selling investments can have tax implications. Be sure to consider the tax consequences of these decisions before making them.
14. Staying informed of tax changes and their impact on financial planning.
Tax laws and regulations frequently change, making staying on top of the latest tax changes challenging. Staying informed about tax changes can help you plan and make smart financial decisions throughout the year.

Penalties and Consequences of Failing to File or Pay Taxes Correctly
Failure to file or pay taxes correctly can result in penalties and consequences that can be financially and personally devastating. Below, we have listed the penalties you may encounter if you fail to file your taxes.
- Interest on Late Payments
One of the consequences of failing to make sure taxes are correctly withheld is the interest on late payments. The interest rate is compounded daily and can quickly accumulate, making paying off the tax debt challenging.
- Compromise Penalty
A compromise penalty is a penalty for failing to file a return or for filing a return late. The compromise penalty can be negotiated with the BIR, but it is not always guaranteed.
- Surcharge Penalty
A surcharge penalty is a penalty for failing to pay the correct amount of tax. The BIR can also charge additional interest on the surcharge penalty.
- Criminal Penalties
Failing to file or pay taxes correctly can also result in criminal penalties. Tax fraud or evasion can result in fines and imprisonment. The penalty depends on the amount of tax involved, the time you fail to pay the taxes, and your intent.
- Interest on Deficiency Tax
Interest on deficiency tax is another consequence of failing to file or pay taxes correctly. The interest rate on deficiency tax is 20% per annum from the date the tax became due. The interest on deficiency tax is compounded daily and can quickly accumulate, making it challenging to pay off the tax debt.
- Garnishment of Bank Accounts and/or Real Property
The BIR can also garnish bank accounts and/or real property to collect taxes owed. This means that the BIR can freeze a taxpayer’s bank account or seize their property to collect unpaid taxes.
- Disallowance of Tax Credits or Deductions
Failing to file or pay taxes correctly can also result in the disallowance of tax credits or deductions. This means that you may lose the right to claim certain tax credits or deductions, resulting in a higher tax liability.
- Loss of the Right to Claim a Refund
Failing to file or pay taxes correctly can also result in the loss of the right to claim a refund. If the taxpayer fails to file a tax return, they may lose the right to claim a refund even if they overpaid their taxes.
- Civil Penalties
Civil penalties can also result from failing to file or paying taxes correctly. These penalties can be assessed for failure to file an accurate tax return.
- Tax Assessments
The BIR can also determine the correct amount of tax owed if the taxpayer fails to file a tax return. This is called a tax assessment, and it can result in additional tax liability, penalties, and interest.
- Warrant of Distraint and/or Levy
The BIR can also issue a Warrant of Distraint and/or Levy, which allows them to seize assets to collect taxes owed. This means that the BIR can take a taxpayer’s property, such as a car or a house, to pay off their tax debt.
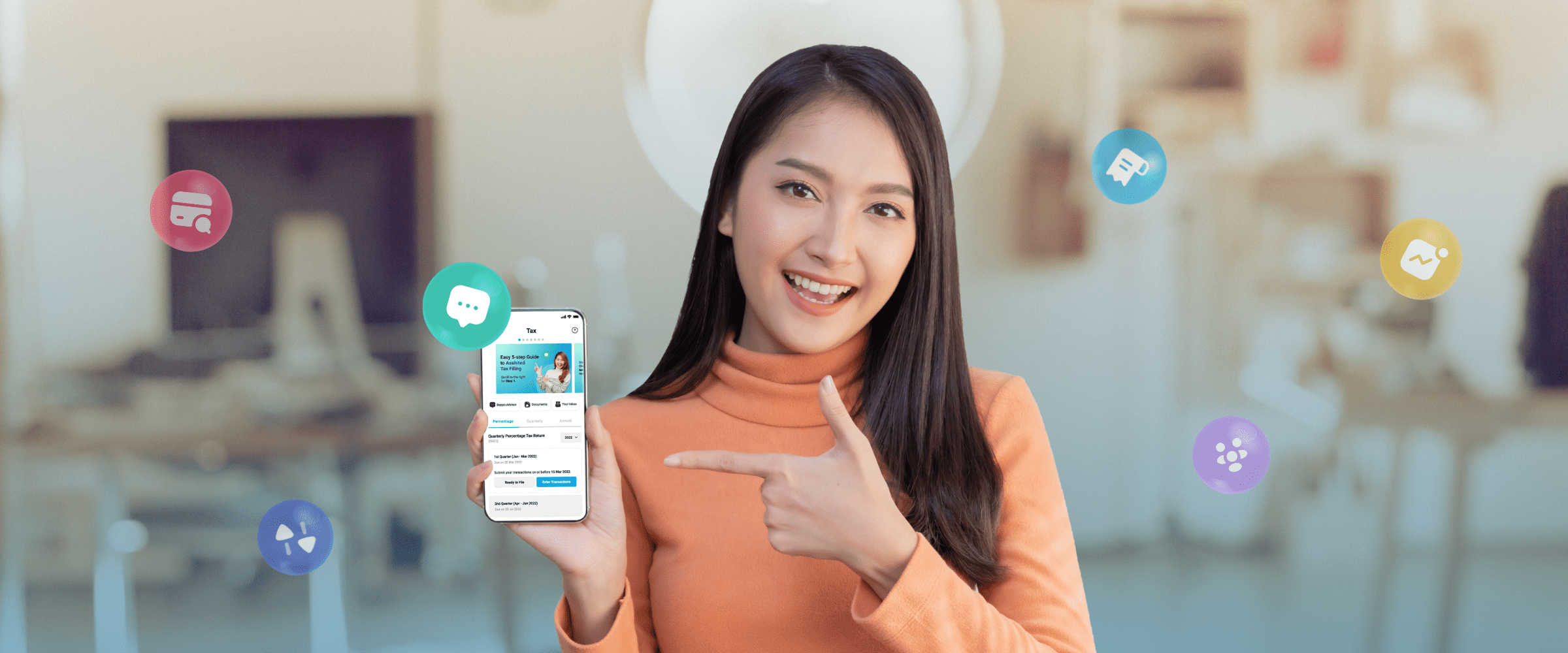
Filing Your Tax Can be a Breeze with Beppo
Filing your income tax return as a resident citizen in the Philippines is essential for freelancers. It may seem daunting initially, but it can be a straightforward process with the correct information and guidance. Fortunately, apps are available to help you with the electronic filing of your income tax return.
With the Beppo App, freelancers like you can leverage an all-in-one financial management platform that makes tax filing more convenient and manageable. Beppo allows you to track money and projects, file and pay your taxes, and send client invoices in the most hassle-free way.
Instead of the usual 12-step process, Beppo allows you to file your ITRs in three easy steps:
- Record your transactions
- Receive and review your tax returns
- File and pay the amount
Other features also include:
- Track and manage your income and expenses
- Send client invoices through various channels such as SMS, Viber or email
- Set limits and automate your budget
- Get estimates of your taxes
- Connect and engage with other freelancers
- Get assistance when filing your taxes
Get started on automating your tax and finances. Connect with Beppo to know more. Or visit our website https://beppo.com.

